Dr. Jacob specializes in primary and revision hip replacement surgery. He uses advanced techniques including minimally invasive surgery and robotic-assisted technologies to improve patient outcomes
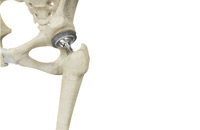
Total Hip Replacement THR
Total hip replacement is a surgical procedure in which the damaged cartilage and bone is removed from the hip joint and replaced with artificial components. The hip joint is one of the body's largest weight-bearing joints, located between the thigh bone (femur) and the pelvis (acetabulum). It is a ball and socket joint in which the head of the femur is the ball and the pelvic acetabulum forms the socket. The joint surface is covered by a smooth articular cartilage which acts as a cushion and enables smooth movements of the joint.
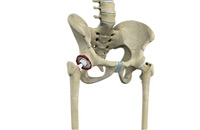
Revision Hip Surgery
Revision hip replacement is a complex surgical procedure in which all or part of a previously implanted hip-joint is replaced with a new artificial hip-joint. Total hip replacement surgery is an option to relieve severe arthritis pain that limits your daily activities. During total hip replacement the damaged cartilage and bone is removed from the hip joint and replaced with artificial components. At times, hip replacement implants can wear out for various reasons and may need to be replaced with the help of a surgical procedure known as revision hip replacement surgery.
Non-surgical Treatment of Hip
The hip joint is a ball and socket joint and is the largest weight-bearing joint in the human body. The head of the thigh bone or femur forms the “ball” and the acetabulum of the pelvis is the “socket”. These bones join together to form the hip joint.
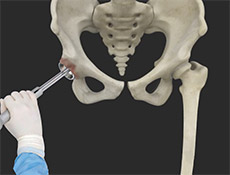
Robot-assisted Hip Replacement
We understand that making sure you know what to expect from the joint replacement experience is important to you. As you are reading through this material, if you have additional questions please reach out to us to discuss.
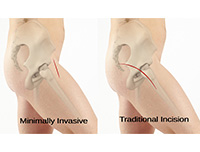
Minimally Invasive Approaches to the Hip
The hip joint is one of the body's largest weight-bearing joints and is the point where the thigh bone (femur) and the pelvis (acetabulum) join. It is a ball and socket joint in which the head of the femur is the ball and the pelvic acetabulum forms the socket. The joint surface is covered by a smooth articular cartilage that cushions and enables smooth movements of the joint.

Partial Hip Replacement
The hip joint is one of the body's largest weight-bearing joints and is the point where the thigh bone (femur) and the pelvis (acetabulum) unite. It is a ball and socket joint in which the head of the femur is the ball and the pelvic acetabulum forms the socket. The joint surface is covered by a smooth articular cartilage that cushions and enables smooth movements of the joint.
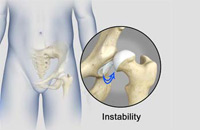
Hip Instability
The hip plays an important role in supporting the upper body weight while standing, walking and running, and hip stability is crucial for these functions. The femur (thigh bone) and acetabulum (hip bone) join to form the hip joint, while the labrum (tissue rim that seals the hip joint) and the ligaments lining the hip capsule maintain the stability of the hip. Injury or damage to these structures can lead to a condition called hip instability. Hip instability happens when the hip joint becomes unstable causing various symptoms.
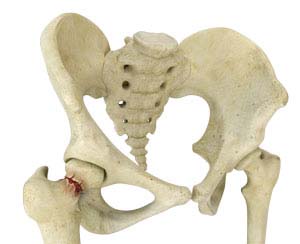
Hip Fracture
The hip joint is a “ball and socket” joint. The “ball” is the head of the femur, or thigh bone, and the “socket” is the cup shaped acetabulum. The joint surface is covered by a smooth articular surface that allows pain free movement in the joint.
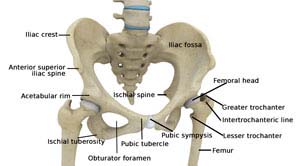 The thigh bone, femur, and the pelvis, acetabulum, join to form the hip joint. The hip joint is a “ball and socket” joint. The “ball” is the head of the femur, or thigh bone, and the “socket” is the cup shaped acetabulum.
The thigh bone, femur, and the pelvis, acetabulum, join to form the hip joint. The hip joint is a “ball and socket” joint. The “ball” is the head of the femur, or thigh bone, and the “socket” is the cup shaped acetabulum.
The joint surface is covered by a smooth articular surface that allows pain free movement in the joint.
The cartilage cushions the joint and allows the bones to move on each other with smooth movements. This cartilage does not show up on X-ray, therefore you can see a “joint space” between the femoral head and acetabular socket.
Pelvis
The pelvis is a large, flattened, irregularly shaped bone, constricted in the center and expanded above and below. It consists of three parts: the ilium, ischium, and pubis.
The socket, acetabulum, is situated on the outer surface of the bone and joins to the head of the femur to form the hip joint.
Femur
The femur is the longest bone in the skeleton. It joins to the pelvis, acetabulum, to form the hip joint.












